Blog
What Is Pad Printing? Everything You Need to Know

As a company which focuses on the sticker printing industry and addresses any printing-related issues, CustomAny is here for those who are interested in printing or finding a suitable printing method for your needs.
Today, let’s explore pad printing – a versatile and widely-used printing technique that’s essential in many fields. Along this blog post, you will be equipped with a deep understanding of “what is pad printing” and how it can enhance the way you approach printing projects.
Let’s discover!
1. What is Pad Printing
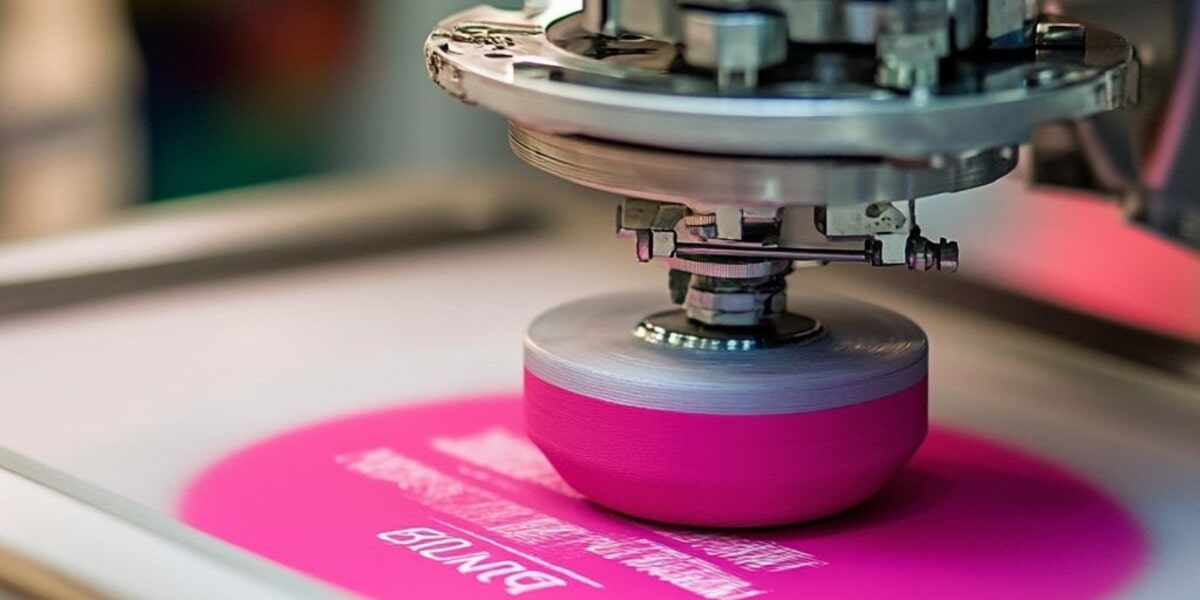
Pad printing is a versatile printing method that transfers images onto objects, particularly those with irregular surfaces. This technique uses a silicone pad to pick up ink from an engraved plate and then press it onto the target object.
The pad’s flexibility allows it to conform to the shape of the object, making it possible to print on surfaces that are difficult or impossible for other printing methods, such as:
- Curved
- Concave
- Convex
- Textured
During pad printing, a single color is printed per face of the object. The object is then rotated or repositioned, and the process is repeated with a different color. This means pad printing can involve numerous printing steps to achieve multi-colored designs.
2. How Pad Printing Works
About pad printer
A pad printer is a specialized machine used for transferring 2D images onto 3D objects. It is often box-shaped or cylindrical, with a platform for holding the object to be printed.
This machine is commonly made of durable materials such as steel, aluminum, and high-quality plastics.
A pad printer typically consists of several key components:
- A printing plate, which holds the etched image that will be transferred.
- A silicone pad, often made from soft silicone. It picks up and transfers the inked image.
- An ink cup, which contains ink. And it applies ink to the printing plate.
- A doctor blade: Scrapes away excess ink from the printing plate, leaving ink only in the etched areas.
Pad printing process
Step 1: Preparing
As a first step, the printing plate is created by transferring the desired image onto a plate typically made of steel or polymer. The image is etched onto the plate using various methods such as laser engraving or chemical etching. This creates recessed areas on the plate that will hold the ink for transfer.
Step 2: Applying ink
- After the preparation step, the plate is inked.
- Then, ink is applied onto the etched image on the plate with the ink cup.
- The doctor blade then passes over the plate, removing excess ink while leaving the ink in the recessed areas. This process ensures that only the intended image will be transferred.
Step 3: Transfering image to the Pad
In this step, the pad presses against a plate to pick up ink from the etched designs.
The silicone material of the pad is key because it’s soft and flexible, allowing it to conform to the contours of the etched areas, ensuring a clean pickup of the ink. The pad’s flexibility also ensures that it can lift the ink evenly across the entire image, even if the image features fine details or gradients.
Step 4: Transfering image to the object
In the final step, the silicone pad moves to the object to be printed. The pad presses against the object, transferring the inked image accurately.
The pad’s flexibility is again crucial here, as it enables the pad to conform to irregular surfaces and varying shapes, ensuring a clean and precise transfer of the image.
3. Types of pad printers
Pad printers come in 3 main types: manual, semi-automatic, and automatic, each offering different levels of automation and efficiency:
Manual pad printers
This type requires the operator to control the entire process manually. In each cycle, the operator needs to load and unload the substrates and move the pads and printing plates. There are no motors or automation systems, making it simple but labor-intensive.
Semi-automatic pad printers
The semi-automatic pad printing machine automates pad and plate movements. The operator typically places the item in position and starts the printing cycle using a button or foot pedal. This setup increases efficiency while still requiring some manual input.
Automatic pad printers
These printer types are fully automated, handling the entire process without manual intervention. The machine automatically takes in objects, prints them on, and moves them out. Advanced models can perform multi-color printing in a single cycle, offering high speed and precision.
Overall, choosing the right type of pad printer depends mainly on the object you want to print, the production volume, available workforce, and your budget.
4. Pad Printing: Pros and Cons
Once knowing more about “what is pad printing”, here are several advantages and disadvantages of this printing method before you choose it:
Pros
Printing on various types of surfaces
Pad printing is ideal for printing on surfaces that may be challenging for other printing methods, such as:
- Curved surfaces
- Textured surfaces
- Uneven surfaces
With the silicone pad, ink can be transferred to a variety of materials and shapes with a high precision.
Offer high-quality prints
With this technique, you can print images with exact details and color even on small or complex items.
The flexibility allows the pad to pick up the ink from the printing plate and transfer it accurately onto even the most intricate surfaces without distorting the design.
Handling complex designs
Pad printing is capable of managing complex designs that involve:
- Overlapping colors
- Gradients
- Or intricate patterns.
The printing process can accommodate detailed artwork that requires precise color registration, ensuring that even multi-color designs are accurately reproduced.
Economical for small quantities
Compared to traditional methods like screen printing, pad printing is more economical for small production runs.
The setup process is simpler and quicker because of the flexible silicone pads and relatively low-cost of pad printing plates. This makes pad printing an attractive option for those needing to print small batches without spending high setup costs.
Cons
Printing multi-colors requires a long process
Since each color is printed individually, complex designs with multiple colors can be time-consuming, which slows down the production process.
Limited to certain surface sizes
In pad printing, the printing plate size directly determines the maximum area that can be printed in a single pass.
Similarly, the silicone pad must be appropriately sized to pick up the entire image and transfer it accurately.
This size limitation can restrict the application of pad printing to items.
5. Common Applications of Pad Printing
Pad printing machines are widely used across various industries due to their ability to print on irregular surfaces and achieve fine detail. Their common applications are in the production of:
- Promotional items like pens, mugs, and keychains, where logos and branding are often applied.
- Electronics industry for marking keyboards, switches, and other small components that require precise, durable labeling.
- Toy industry for adding detailed decorations, such as eyes or intricate designs on action figures.
- Printing directly onto clothing, especially for tagless labels on garment
- Marking devices and products where precision and clarity are crucial.
- ….
Last words
In conclusion, we have delved deep into “what is pad printing”, uncovering its versatility, precision, and wide-ranging applications across various surfaces. Pad printing offers precise, high-quality results on everything from promotional items to complex electronic components.
For further reading, explore our website’s blog page on other printing techniques like screen printing, sublimation, digital printing… Our comprehensive guides will help you be confident in your printing choices.